DFGGFGFGG
dhdhhdhhd
We are convinced that the average investor cannot deal successfully with price movements by endeavoring to forecast them. -Benjamin Graham
dfhfghhgfghfgh
Late in 2025, I stated I would devote a blog and podcast to dollar-cost averaging. I feel that dollar-cost averaging is one of the two most important strategies that do-it-yourself investors can implement. The second strategy is periodic rebalancing of portfolio accounts.
You’ll notice that I termed dollar-cost averaging and periodic rebalancing as strategies. These are not core principles that are used to build a retirement plan or design a portfolio. They are strategies that will help to optimize your plan!
It is not uncommon for do-it-yourself investors to jump ahead by implementing these strategies, while ignoring or minimizing the planning, design, and implementation of retirement plans.
These core steps are necessary before moving to strategies that increase portfolio efficiency!
In the past I did a blog and podcast on portfolio rebalancing called STRIKING THE PERFECT BALANCE: THE ART OF PORTFOLIO REBALANCING, so this blog and podcast will focus on dollar cost averaging.
It’s worth noting that I employed both of these strategies with my personal investments for many years. Additions to my retirement plan are nominal, so I no longer use dollar-cost averaging. I now make small annual contributions to my SEP IRA. This doesn’t mean that I have lost faith in the power of Dollar-Cost Averaging. Because the dollar amounts that I now invest are so small, it’s not worth the time and effort to dollar-cost average.
I do, however, still rebalance periodically and feel that both strategies are important and relevant.
cbcbbbbc
WHAT IS DOLLAR COST AVERAGING?
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) is an investment strategy where an individual invests a fixed amount of money in a particular security (such as stocks, mutual funds, or ETFs) at regular intervals. Investments are made regardless of the share price. This systematic approach aims to reduce the impact of market volatility and help build disciplined investing habits over time.
By investing a consistent dollar amount each time, more shares are purchased when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high. This can result in a lower average cost per share over time compared to investing a lump sum all at once.
An example of dollar-cost averaging is contributing a fixed amount from each paycheck to a workplace retirement plan.
dhdhhdhd
Pros and Cons
Advantages
Reduces emotional investing: Investing a fixed amount periodically, regardless of market valuations reduces emotional decisions. DCA reduces market timing behavior. Mitigates volatility and timing risk: Spreads out the risk of investing a large sum right before a market downturn or peak. Builds discipline: Periodic consistent contributions create a long-term investing habit. Average cost per share: Buying more shares at lower prices can lower the average cost per share
ghgdggdgd
Disadvantages
Potential for lower returns: In a consistently rising market, lump-sum investing often outperforms DCA because all capital is put to work sooner. Opportunity cost: Uninvested money held in cash vehicles like Money Market funds, usually earns lower returns. Transaction fees: Transaction fees are a lesser concern now, as most trades are commission-free.
cgggcggcggc
Is Dollar Cost Averaging Right For You
Dollar-cost averaging is a powerful tool, especially for new investors or those who prioritize risk management and peace of mind over maximizing every potential return. It is an effective strategy when used to invest in long-term diversified assets such as index funds and ETFs. However, it does not guarantee a profit or protect against losses in declining markets.
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) is a strategy that aims to reduce market timing risk, not necessarily to achieve a specific “expected Alpha” in the formal financial sense. Instead of trying to beat the market, it focuses on reducing the average cost per share by investing a fixed amount regularly, which can lead to a higher number of shares purchased over time, particularly in volatile markets.
cbcgvgc
How Dollar Cost Averaging Works
- You invest a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the market’s current price.
- When prices are high, your money buys fewer shares.
- When the prices are low, your money buys more shares.
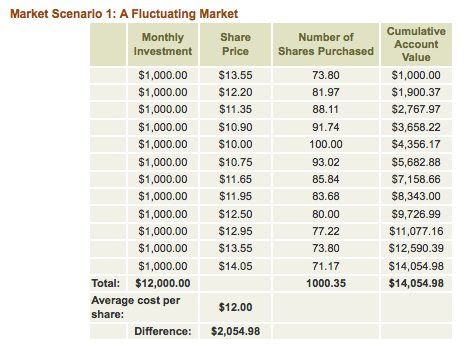
- This process can lead to a lower average cost per share than investing a lump sum at once, especially in a fluctuating market.
dhdhhhd
Benefits of DCA
- It can lower the average amount you spend on investments.
- It reinforces the practice of investing regularly to build wealth over time.
- It’s automatic and can take concerns about when to invest out of your hands.
- It removes the pitfalls of market timing, such as buying only when prices have already risen.
- It can ensure that you’re already in the market and ready to buy when events send prices higher.
- It takes emotion out of your investing and prevents you from potentially damaging your portfolio’s returns.
xhdhhdhhd
Example of DCA
Jordan works at ABC Corp. and has a 401(k) plan. Jordan receives a paycheck of $1000 every two weeks and allocates 10% ($100) to his employer’s plan every pay period. He contributes 50% of his stock allocation to a large-cap mutual fund and 50% to an S&P 500 index fund. Every two weeks, 10% ($100) of Jordan’s pretax pay will buy $50 worth of each of these two funds, regardless of the fund’s price. The table below shows half of Jordan’s $100 contributions that went to the S&P 500 index fund over 10 pay periods. Throughout 10 paychecks, Joe invested a total of $500, or $50 per week. Note that the NAV (Net Asset Value) of the fund changed over that time, meaning shares were purchased at higher and lower prices.
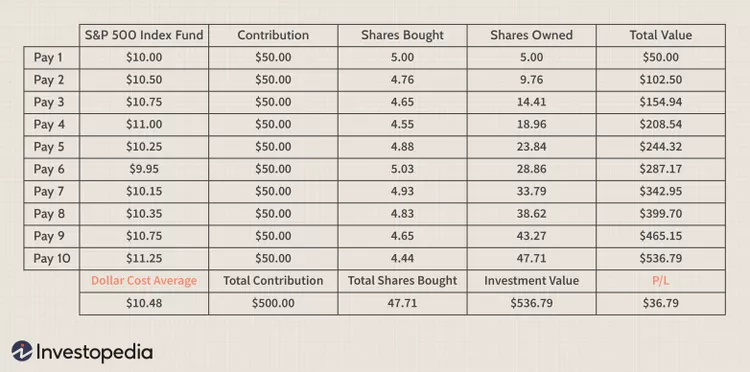
Investopedia / Sabrina Jiang
fhfhhfhhf
How Dollar-Cost Averaging Affects Returns
- Lower return potential: Over the long term, lump-sum investing has been shown to produce higher returns in a majority of scenarios, especially in a rising market.
- Benefit in falling markets: DCA can be beneficial in a volatile or declining market because you buy more shares when prices are low and fewer when prices are high, resulting in a lower average cost per share than a lump-sum invested at the beginning.
- Risk management: The primary advantage is risk reduction. By investing smaller amounts over time, you avoid the risk of investing a large sum right before a market downturn.
- Emotional benefits: DCA can help prevent emotional decision-making. It removes the pressure of timing the market and can alleviate the regret of a poorly timed investment.
dhdhhhd
When Dollar-Cost Averaging is Most Useful
- You don’t have a lump sum: It is a practical strategy when you have a windfall like an inheritance and can’t invest it all at once, or for regular investments like retirement contributions.
- You are risk-averse: DCA provides a measured approach if the concern is losing money in the short term, .
- You need a strategy to follow: It’s an easy, automated way to invest that removes the need for market timing and can be set to run consistently.
- The Market is Declining: Dollar-cost averaging is most effective when the market is declining. A continually declining market causes more shares to be purchased with the same amount of money. This reduces the overall average cost per share.
dhdggdhhd
dhdgghgdghhd
Final Thoughts
DCA is a disciplined strategy for long-term investors that prioritizes consistency over market timing.
Lowering average cost per share can build wealth gradually, but does not guarantee a positive alpha and could result in lower returns than lump-sum investing in certain market conditions.
The primary benefit of DCA is the reduction of risk and emotional decision-making. DCA does not necessarily achieve an expected higher return.
There is an ongoing debate about which strategy is better: lump-sum investing or dollar-cost averaging. My next blog and podcast will compare dollar-cost averaging to lump-sum investing.
dhdhhhdh
dbnhhdbhbd
If you’d like to be a part of a free online retirement community, join us on Facebook:
COMMENTS